Endovenous (or vein) ablation is a minimally invasive outpatient treatment for venous insufficiency that is performed using ultrasound guidance. After applying local anesthetic to the skin over the vein, an interventional radiologist inserts a thin tube known as a catheter, about the size of a strand of spaghetti, into the abnormal saphenous vein. Through this catheter, laser or radiofrequency energy is applied to the inside of the vein to seal it closed.
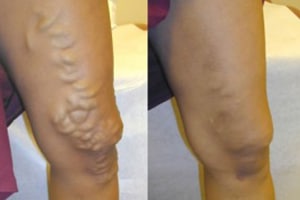
Reflux within one of the saphenous veins can lead to pooling in its tributaries (branches), causing visible varicose veins to develop and more blood for the surrounding normal veins to send back toward the heart. By closing the abnormal vein, the varicose veins—which are close to the skin—shrink and improve in appearance. In addition, once the diseased vein is closed, the surrounding healthy veins are no longer burdened by the leaking blood flow. Other healthy veins take over to carry blood from the leg, re-establishing normal flow.
Benefits of Endovenous Laser / RF Ablation (EVLT)
- The treatment takes less than an hour and provides immediate relief of symptoms.
- Immediate return to normal activity with little or no pain. There may be minor soreness or bruising, which can be treated with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- No scars or stitches – because the procedure does not require a surgical incision, just a nick in the skin, about the size of a pencil tip.
- High success rate and low recurrence rate compared to surgery.
- The success rate ranges for vein ablation ranges from 93-97 percent.
Laser Surgeries / Endovenous Laser Treatment
Doctors are using new technology in laser treatments to close off smaller varicose veins and spider veins. Laser surgery works by sending strong bursts of light onto the vein, which makes the vein slowly fade and disappear. No incisions or needles are used.
Endovenous laser treatment
Endovenous laser treatment is a minimally invasive technique to destroy the greater saphenous vein (GSV) in the thigh and/or the small saphenous vein (SSV) at the back of the calf.
Laser is an acronym and stands for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Laser light is monochromatic (single wavelength) light produced from a laser medium and then amplified to produce a powerful beam
There are at least 5 types of laser available all with the supporters and detractors. The different lasers vary in the wavelength of the laser light produced and there are some theoretical advantages and disadvantages of each of these different types of lasers. There is little evidence to support one laser over another and there is no level 1 evidence from blinded randomized trials. Presently there are lasers working at 810, 940, 980, 1320 and 1470nm. EVLT™ is a particular brand of device that is used for EVLA.
How EVLA & RFA Is Performed
These techniques are very similar but there are some minor differences.
The first part of the procedure involves inserting a catheter (fine tube) into the vein to be treated (cannulation). This is usually done by using ultrasound to guide a fine hollow needle into the vein. A wire is then passed into the vein through the hollow of the needle and the needle removed along the wire. The wire is then passing from outside the skin into the vein. The hollow catheter is then threaded on to the part of the wire on the outside and passed along the wire into the vein. Once the catheter is in position the wire is removed. This is known as the Seldinger technique and is a common method of obtaining access to many structures in the body. Ideally the catheter should be positioned down the leg as far as the abnormal flow is present. If necessary a small incision can be made to obtain access to an appropriate vein if this is difficult using the ultrasound technique.
The radiofrequency catheter/laser fiber is then passed up the vein and positioned no closer than 2cms from the saphenofemoral or saphenopopliteal junctions. These are junctions between the superficial and the deep veins and the distance is to minimize the possibility of damage to the deep veins, but maximize the length of vein to be treated. The video below is an animation of the technique.

 Wearing
Wearing