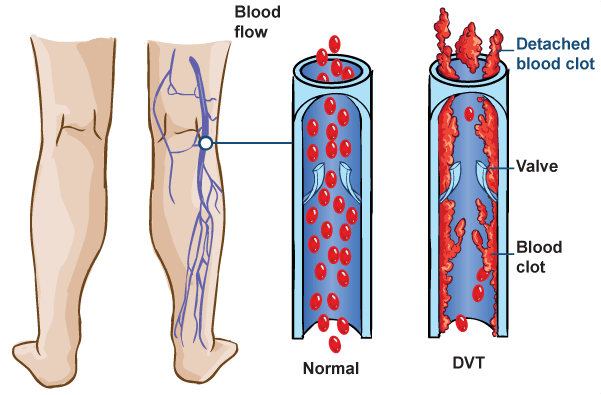
Introduction
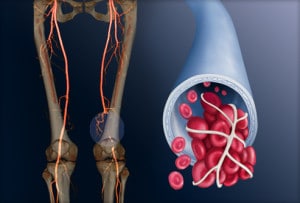
A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in the deep large veins of the pelvis, legs, thighs, or arms. A DVT can reduce or block the flow of blood in a vein. It may dislodge and travel in the bloodstream, causing a stroke, pulmonary embolism, heart attack, or death. DVT is a potentially life-threatening condition and requires immediate medical attention. DVTs may be treated with medications or surgery.
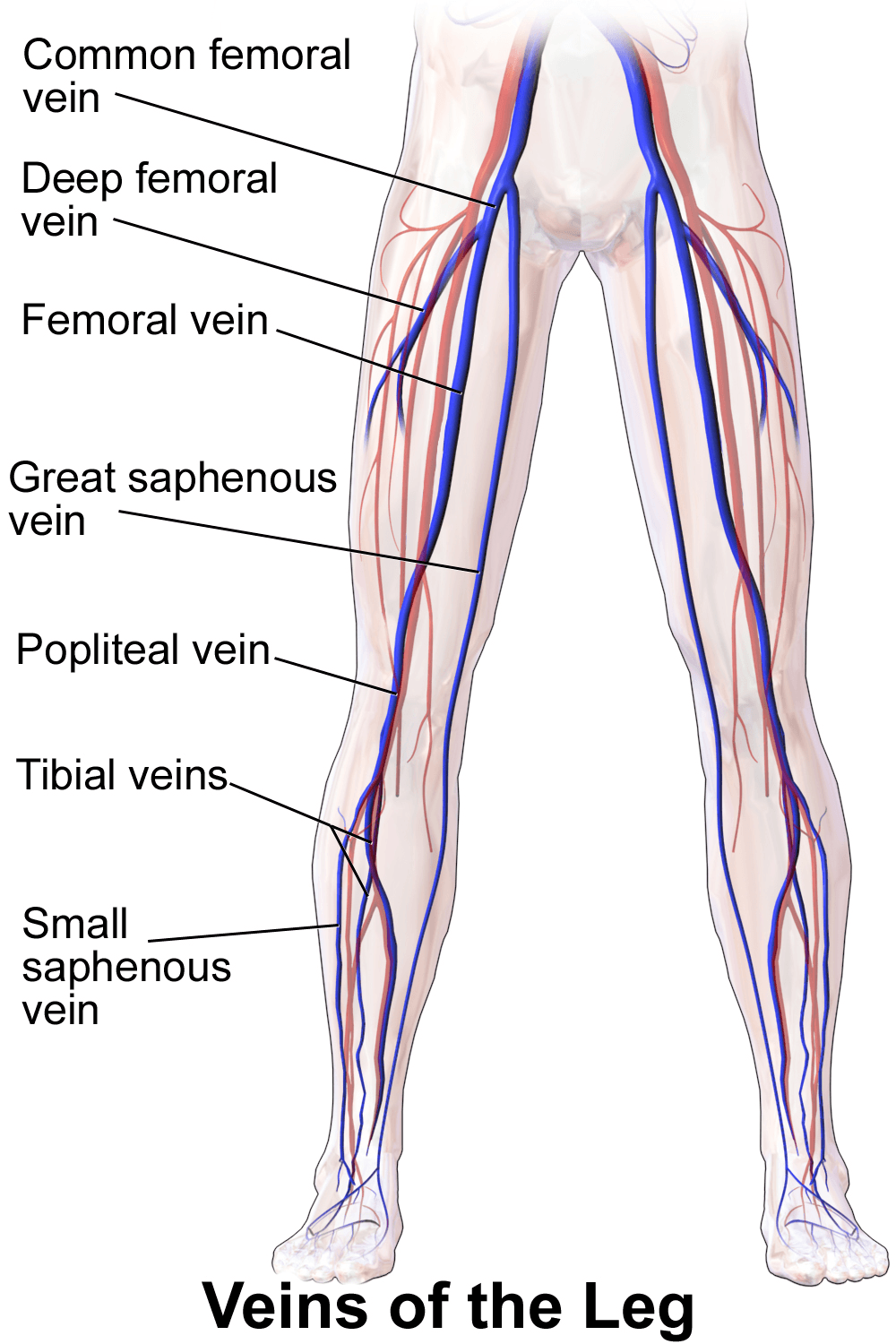
Anatomy
The heart has several large arteries and veins connected to it that branch out and become smaller as they travel throughout your body. Your arteries and veins are blood vessels that deliver blood throughout your body in a process called circulation. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from your heart. Veins carry deoxygenated blood from your body and lungs back to your heart.
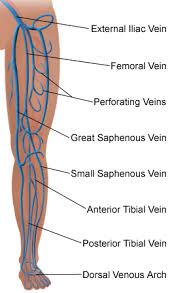
Causes
DVTs can occur in the deep large veins of the pelvis, legs, thighs, or arms. They may develop after prolonged bed rest or immobility, such as after long plane or car trips. Risk factors may increase the likelihood of DVT development.
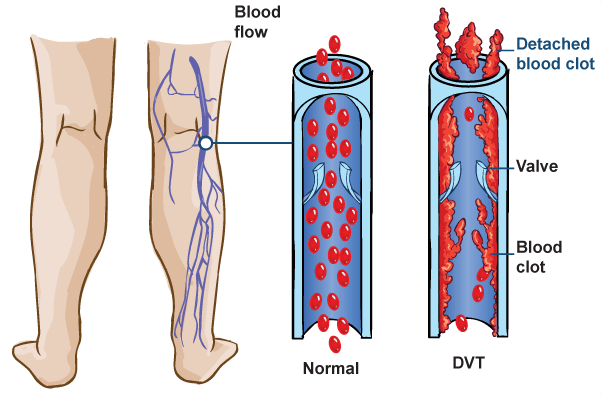
Symptoms
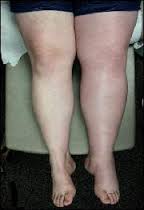
A DVT can cause pain or tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling. A DVT in the leg may cause the one leg to swell, discolor, and cramp like a “charlie horse.” A DVT in the arm may cause upper arm or neck swelling.
Diagnosis
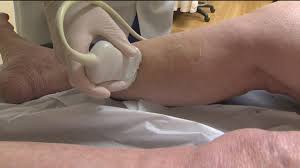
You should contact your doctor immediately if you suspect that you have a DVT. Your doctor will examine you and conduct some tests to determine if a clot is present. If a clot is present, your doctor will determine the severity of the clot. Blood tests and imaging tests are commonly conducted. A Doppler ultrasound of the legs may identify a blood clot by using sound waves to create an image when a device is gently placed on your skin. A venography is used to identify blood clots in a procedure that uses X-rays and dye administered through a catheter that is inserted into a vein. You may receive a general or local anesthesia for the procedure. An impedance plethysmography is a non-invasive blood circulation test used to detect the presence of a blood clot. It may be used as an alternative to a venography.
Treatment
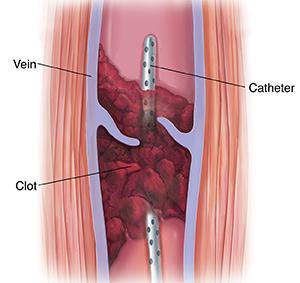
DVTs may be treated with blood thinning medications called anticoagulants or clot busting medications termed thrombolytic therapy. In some cases, clots are removed with a catheter or surgery. People that cannot tolerate or do not respond to anticoagulation may have a permanent filter inserted in their vein. The filter prevents large embolisms from entering the lungs but it does not stop blood clots from developing.
Am I at Risk?
Risk factors may increase your likelihood of developing DVT, although some people that develop the condition do not have any risk factors. People with all of the risk factors may never develop DVT; however, the chance of developing the condition increases with the more risk factors you have. You should tell your doctor about your risk factors and discuss your concerns.
A Solution For Blood Clots
 Precision specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of blood clots within both the deep and superficial venous system. Blood clots often cause pain and swelling of the affected limb and can be a life-threatening condition. Blood clots rarely dissolve completely on their own and can often lead to permanent damage of the veins and possible life-long side effects called post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS).
Precision specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of blood clots within both the deep and superficial venous system. Blood clots often cause pain and swelling of the affected limb and can be a life-threatening condition. Blood clots rarely dissolve completely on their own and can often lead to permanent damage of the veins and possible life-long side effects called post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS).
Although many doctors treat patients for Deep Vein Thrombosis or (DVT) and blood clots, we specialize in comprehensive DVT and blood clot care by offering minimally invasive therapy to potentially remove or dissolve blood clots in the body, especially in the legs. By undergoing an evaluation with one of our experts, you can ensure that your Deep Vein Thrombosis is being treated with the most advanced therapies and techniques available.
 Our office has a vascular ultrasound lab capable of performing the important ultrasound tests to check for blood clots within the legs or the arms. Our experts are experienced in the most advanced, state-of-the-art treatments for Deep Vein Thrombosis, including outpatient procedures used to dissolve and remove the clot within the legs.
Our office has a vascular ultrasound lab capable of performing the important ultrasound tests to check for blood clots within the legs or the arms. Our experts are experienced in the most advanced, state-of-the-art treatments for Deep Vein Thrombosis, including outpatient procedures used to dissolve and remove the clot within the legs.
The American Heart Association has made strong recommendations that any patient with certain types of blood clots (iliofemoral) should undergo the Thrombolysis procedure. Therefore, any patient diagnosed with a blood clot should be seen by a vascular specialist trained in the full range of treatment options.
Important Points To Consider When Choosing A DVT Specialist:
- Our office provides comprehensive care for DVTs, including: diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up.
- We are one of the few groups in Dallas who can perform the thrombolysis procedure, which can dissolve newly diagnosed blood clots within the body. The thrombolysis procedure has been strongly recommended by the American Heart Association.
- Time is important! The best results arise from blood clots that are treated immediately or within a few weeks after diagnosis.
- Even patients who are suffering from chronic swelling or PTS can often be helped by proper treatment.
- Most insurances cover all diagnostic tests and therapeutic procedures for DVT care.
- Getting expert care for DVTs today can prevent long-term complications such as post-thrombotic syndrome caused by inadequate treatment of a DVT.
- Many patients have significant reduction in the swelling of their legs or arms immediately after getting proper treatment.
At Precision VIR, Excellent Patient Care Is Our Passion
Our specialists will take the time to answer your questions about Deep Vein Thrombosis and our advanced procedures. If your veins need treatment, request an appointment for an evaluation with the experts at Precision VIR. We will create an individualized plan to help you get the best results.
F.A.Q.